We all use them daily, but have you ever truly wondered how search engines like Google, Bing, and DuckDuckGo navigate the vast ocean of the internet to deliver the exact answers you crave?
Let’s dive into the fascinating world of search engines, their inner workings, and how they make finding information (and sometimes cat videos) seem effortless.
Search Engine Basics
What are Search Engines?
Search engines are programs that help people find information on the internet.
They use algorithms to index web pages and match them with the user’s search query.
Search engines also provide additional features such as personalized search results, suggested searches, and specialized search filters.
Think of them as digital librarians, constantly crawling the web and organizing information into massive indexes.
They’re made up of two main parts:
- Search index: A digital library of information about web pages.
- Search algorithm(s): Identifies matching results from the search index using computer programs.
What’s the Aim of Search Engines?
To provide the most relevant and helpful results for your queries as quickly as possible.
To achieve this, search engines use complex algorithms to analyze webpages and rank them according to various factors, such as relevance, popularity, and authority.
This helps to ensure that users are provided with the most relevant results for their queries.
How do Search Engines Make Money?
Search engines generate revenue by displaying ads on search results pages.
These ads are targeted based on the user’s search query and the content on the page. Advertisers pay search engines based on clicks, impressions, or other metrics.
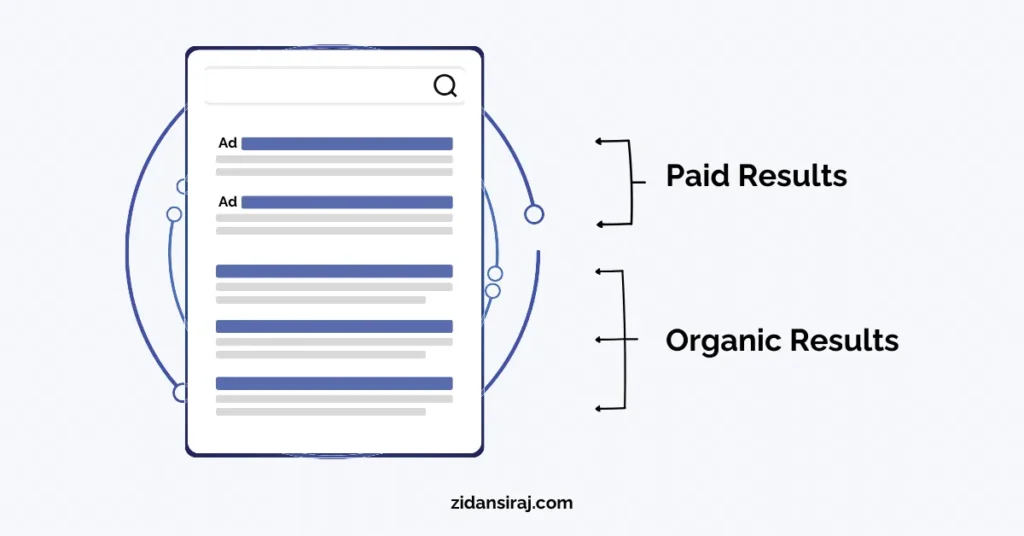
Search engines have two types of search results:
- Organic results from the search index. You can’t pay to be here.
- Paid results from advertisers. You can pay to be here.
How do Search Engines Build their Indexes?
Search Engines use algorithms to crawl web pages and store them in their indexes.
The algorithms are designed to identify and rank relevant web pages based on their relevance and importance.
The indexes are then used to return search results when a user searches for something.
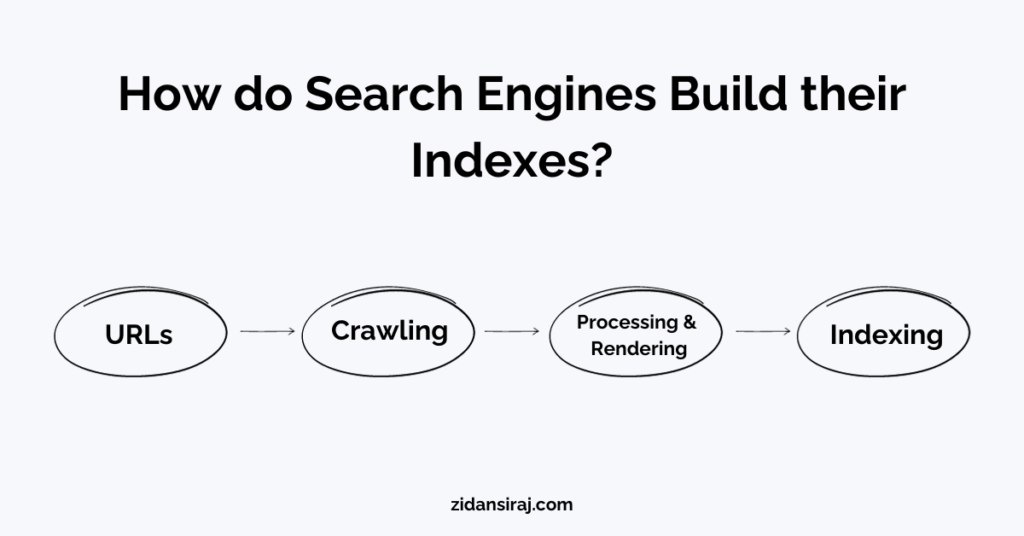
URLs
Search engines identify and track each website by its unique address (URL).
It all starts with a known list of URLs. Google discovers these in many ways, but the three most common are:
- From backlinks. The Google index contains hundreds of billions of webpages. If someone links to a new page from a known page, Google can find it there.
- From sitemaps. Google uses sitemaps to determine which pages and files your site is important.
- From URL submissions. Google lets site owners request crawling of individual URLs in Google Search Console.
Crawling
Imagine tireless bots following website links, discovering new pages, and updating the index. Google’s crawler is Googlebot.
Crawlers are an essential part of Google’s search engine, as they help Google index web pages and determine their relevance for search users.
Crawlers are also used to detect errors and malicious content.
Processing and Rendering
The bots analyze each page, understanding text, images, and code.
Nobody outside of Google knows every detail about this process. But it doesn’t matter.
We need to know that it involves extracting links and storing content for indexing.
Indexing
All the analyzed information is stored in a massive index, like a library catalogue for the web.
When you use a search engine, you are searching the search index.
That’s why getting indexed in search engines like Google and Bing is so important.
Users can only find you if you’re in the index.
How Search Engines Rank Pages
Search engines use algorithms to rank pages based on several factors, including keywords, content, and backlinks.
This ranking system helps to ensure that the most relevant pages are returned to users when they search for something.
Search Algorithms
Complex programs that analyze your query and compare it to the indexed pages.
Search algorithms are designed to return the most relevant results as quickly as possible.
They use techniques like natural language processing, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to classify and refine search results.
Key Google Ranking Factors
Nobody knows all of Google’s organic ranking factors. However, some factors are known to be important.
Backlinks
Think of them as votes of confidence. Websites with many high-quality backlinks rank higher.
Backlinks also help to increase website visibility. They allow search engines to recognize websites that are important and trustworthy. They can also help to increase website traffic.
It’s not all about quantity, though. Quality matters, too. Often, pages with a few high-quality backlinks outrank those with many low-quality backlinks.
Relevance
How closely does the page content match your query?
Relevance refers to how beneficial a search result is for the user. Google has many ways of determining this.
At the most basic level, it looks for pages with the same keywords as the search term.
Furthermore, it analyzes interaction data to determine whether others found the helpful result.
Freshness
Up-to-date information generally trumps outdated content. Freshness is a query-dependent ranking factor.
It’s stronger for searches that call for fresh results.
Google also considers the content’s age, so newer content is more likely to be ranked higher.
It’s essential to keep content up to date to ensure high rankings.
Page Speed
Nobody likes a slow website; fast loading times get rewarded.
Page speed is essential for user experience.
Faster websites have higher conversion rates, making users more likely to complete tasks.
Poor page speeds can also decrease search engine rankings.
Mobile-friendliness
With most searches happening on phones, mobile-optimized sites get a boost.
Oberlo says searches on mobile phones (64%) are significantly higher than searches on desktops (35%).
Google tailors search results for each user. This is done by using information such as your location, language, and search history. Let’s take a closer look at these things.
How Search Engines Personalize Results
Location
Search engines use location information to tailor search results to the user’s location.
“Best pizza near me” will deliver different results in New York than in Mumbai.
Language
Search engines use language analysis to personalize results. They analyze the user’s search query, the language they use, and the context of the query.
Search in French? You’ll get French results, n’est-ce pas?
Search History
Search Engines use search history to personalize results. This includes cookies, saved searches, and other user data.
Search engines also consider user location and device type when personalizing results.
Ever Googled “best hiking boots”? Expect similar suggestions in the future.
Key Takeaways
- Search engines consist of two main parts: index and algorithms.
- To build its index, it crawls known pages and follows links to find new ones.
- Search algorithms aim to return the most accurate, most relevant results.
- Search result quality is key for building market share.
- Nobody knows all of Google’s organic ranking factors.
- Several factors influence ranking, including backlinks, relevance, and freshness.
- Google personalizes search results according to your location, language, and search history.
References
- “How Search Engines Work“. Search Engine Journal.
- “Trust, Authority & Search Rankings“. Search Engine Land.
- “How Does Google Make Money“. Your Marketing People.
- “What is Indexing?“. Page One Power.
- “SEO Ranking: Factors & Tips to Improve Your Positions“. SEMrush.
- “How website speed affects your conversion rates “. Bidnamic.
- “How Search Engine Personalization Affects Rankings“. Market Brew AI.




